What is Shadow Zone? Seismic Waves & Interior of Earth
Guest Writer/Author: Fazal Firdausi
Defining Shadow Zones
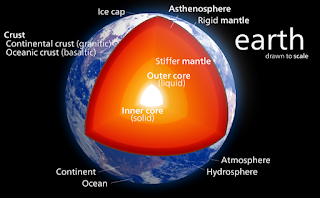
The most important and popular source to know about the interior of the earth is seismic waves i.e., the waves generated during the earthquakes. When an earthquake occurs the seismic waves (Primary and secondary) are spread out in all the directions through the interior. However, there exist specific areas where the waves are not reported. Such zones are called as Shadow Zones.
Properties of the seismic waves and earth’s interior
It is known that Secondary (S) waves cannot pass through liquid medium. The Primary (P) waves can pass through liquid but its velocity is reduced and it gets refracted after entering into liquid medium. When earthquake occurs, both the P & S waves exists up o a depth of 2900 Km from earth’s surface. The S-waves disappears beyond 2900 Km.

It is evident that S-waves are not reported after 103º because outer core is in liquid state. The area between 103º to 103º is known as S-waves shadow zone (see the figure below). P-waves consistently increases its speed till 2900 Km, thereafter it bends due to the presence of liquid in the outer core and emerge at 142º. The area between 103 º to 142 º called as P-waves shadow zone.
Significance of seismic waves to know interior of the earth

The behaviour of seismic waves explains the density differences between different layers of the earth. The scholars have used seismic studies to establish various discontinues (anomalies) existing in the earth viz. Conrad, Mohorovicic, Repiti, Guttenberg and Lehman etc. With the help of seismic wave velocity, we have been able to ascertain the High Velocity & Low Velocity Zones in earth’s interior.
Conclusion
Recent discovery of Large Low sheer velocity provinces (LLVPs) (super plumes) are the result of systematic study of seismic waves. Seismic waves are unearthing newer insights about the earth’s interior and helping us to understand it in a better way.
Reference: Strahler, A.H. & Strahler, A.N. Modern Physical Geography, Wiley, 2008
You may also like: Juno Mission – Revealing the secrets of the Solar System