World Geography – Sudan
Where is Sudan Located?
Sudan is a country in Africa’s northeast. Its latitude and longitude are 12° 86′ North and 30° 21′ East, respectively. It is the third-largest country in Africa and the Arab League in size. Algeria and the Democratic Republic of Congo are larger than Sudan in area. It was the largest country on the African continent until South Sudan’s independence in 2011.
Capital of Sudan: Khartoum
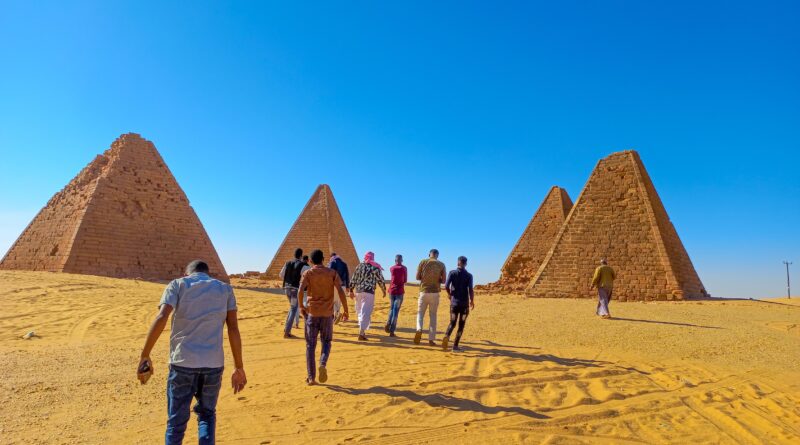
Nubian Pyramids: Sudan has the world’s largest collection of these magnificent old pyramids. Sudan’s ancient Nubian civilization left over 200 pyramids that rise above the desert.
The cultural treasure of Meroe, which is situated around 220 kilometers north of Sudan’s capital Khartoum, is currently one of Sudan’s most important Unesco worldHeritage sites.
Sudan’s neighboring countries:
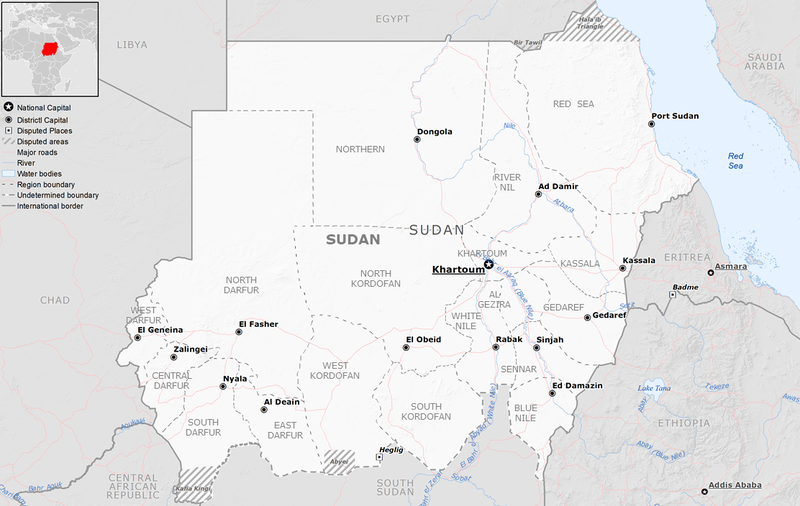
- North: Egypt
- Northwest: Libya
- South: South Sudan
- Southwest: Central African Republic
- East: Eritrea and Ethiopia
- West: Chad
Sudan has access to the Red Sea on its northeastern side.
When Sudan Became a Country?
Before Egypt’s conquest of the region in the early 1800s, Sudan consisted of several small kingdoms. Egypt dominated the northern portions in this period, while the south consisted of independent tribes. Egypt and the United Kingdom established joint control over Sudan in 1898. In 1953, however, the United Kingdom and Egypt accorded Sudan self-government and set it on the path to independence. Sudan achieved independence on January 1, 1956.
Geographical Features of Sudan
The Nile and its tributaries drain the extensive plains and plateaus that make up the majority of Sudan. This river system traverses the entire east-central portion of the country from south to north. Sudan’s vast plain is bordered on the west by the Nile-Congo catchment, the Darfur highlands, and on its eastern side by the Ethiopian Plateau and the Red Sea Hills (Atby). The northern area consists of a rocky desert and undulating dunes, part of the Sahara desert.
Physical Geography of Sudan
It consists of a sizable plain surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Didinga Hills and the Dongotona and Imatong mountains on the southern border, the Red Sea Hills to the east, and Jabal Marrah to the west.

Attribution: Hans Birger Nilsen, CC BY-SA 2.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Northern Sudan:
- Situated near the Egyptian border.
- Mainly rocky and sandy desert.
- Known as the Nubian desert, where there is an absence of oases.
Western Sudan:
- It is called as Darfur and Kurdufan region.
- A flat region where the volcanic massif of Jabal Marrah (900 meters) stands out.
Central Sudan:
- The clay plains that reach east from the Nuba Mountains to the Ethiopian border are interrupted by the Ingessana Hills.
- Sudan’s economy depends on the central clay plains, where many settlements are observed due to water availability.
Drainage:
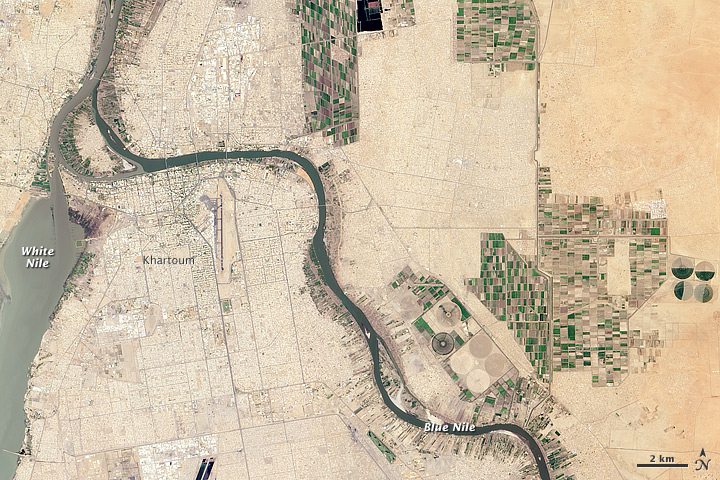

Source: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/images/81186/two-niles-meet
- The Nile River system dominates the landscape of Sudan, and all of its streams and rivers flow into or towards it.
- It enters the nation as the White Nile, around 60 miles (100 km) south of Kūstī. Its gradient is low until Khartoum, where it joins the Blue Nile.
- Most of the White Nile’s waters originate from the Blue Nile, which rises in the Ethiopian Plateau.
- The White and Blue Niles confluence is situated near Khartoum.
Climate:
- Sudan is located in the tropics, but its climate varies from being highly arid in its northern part to tropical wet-and-dry in the southwest.
- Temperatures do not change significantly by season in a large part of Sudan.
- A variation exists in the rainfall and the lengths of the wet and dry seasons.
It is essential for the students to note that the Sudan Type Climate (refer to G.C. Leong) does not exist in the present Sudan (North) anymore; you can observe that climate (Savannah Type) in South Sudan.
Human Geography of Sudan

Population
According to UNFPA, the total population of Sudan is 48.1 million (2023).
People
Sudanese Arabs comprise over 70% of the population, with a sizable black African minority of 30%, including Fur, Beja, Nuba, and Fallata. Sudan’s borders are home to around 500 ethnic communities speaking over 400 languages (mr.org).
Religion
The majority of the people ofSudan are Muslims (Sunni Sect). The followers of Christianity are found in the south and around Khartoum. A small number of Sudanese also follow Animism (Britannica).
Resources
Petroleum
The Upper Nile region is known for its petroleum reserves.
Petroleum export accounts for up to 80% of the total exports, making it one of their most vital sectors. The leading importers of Sudanese oil are India, Indonesia, South Korea, China, and Japan.
Gold
The alluvial gold formation is mined along the Nile and its tributaries, whereas the quartz vein formation is found in the Blue Nile region, Obaidiya, and North Kurdufan.
The significant economic potential of extraction of minerals such as silver, chromite, manganese, gypsum, mica, zinc, iron, lead, uranium, copper, kaolin, cobalt, granite, nickel, tin, and aluminum.
Agriculture
- 1/3 of Sudan’s population depends on agriculture and animal husbandry.
- About one-third of Sudan’s GDP comes from agriculture.
- The principal crops are cotton, peanuts (groundnuts), sesame, gum Arabic, sorghum, and sugarcane.
- Sorghum and millet are the primary subsistence crops, with smaller amounts of wheat, maize, and barley.
Conclusion
Land degradation, rising temperatures, frequent droughts and floods, irregular rainfall, and locust invasions are some of Sudan’s environmental problems. These factors have reduced agricultural output, hindered GDP development, and destroyed livelihoods.
Sudan needs civilian rule, democracy, and economic reforms to streamline its economy and pull people out of poverty.

